What are cannabinoids?
Many people initially associate the plant name "cannabis sativa" with intoxicants. In fact, however, it refers to the so-called common or true hemp. Perhaps the oldest cultivated plant of mankind, it has been used throughout its history as a foodstuff and animal feed as well as in cosmetics. Above all, hemp has become important as a source of so-called cannabinoids - ingredients that have various effects on the human organism.

Hemp - a plant with many faces
Hemp has been known as a cultivated plant for at least five thousand years. In the 18th century, the naturalist Carl von Linné chose the Greek name for hemp, cannabis, to give the entire plant genus a scientific name. Unlike the Indian hemp (Cannabis indica), Cannabis sativa contains few to no intoxicating substances. However, the hemp plant is excellent to cultivate. Hemp fibres can be processed into very resistant fabrics and textiles, but also into paper, ropes, ropes and dressing materials. Hemp is thus an enormously versatile and highly honourable useful plant. More than fifty different varieties of commercial hemp are currently cultivated in Europe. The effects of its most interesting ingredients, the cannabinoids, have been intensively researched for decades. No wonder, then, that hemp-containing products such as hemp seeds, hemp oil or hemp drinks are now widely available.
Cannabinoids - probably the most important ingredients of the hemp plant
Cannabinoids are produced by the metabolism of the hemp plant. At least 113 different substances are currently assigned to this group of substances. The substances and the effects that are discussed in research are:
-
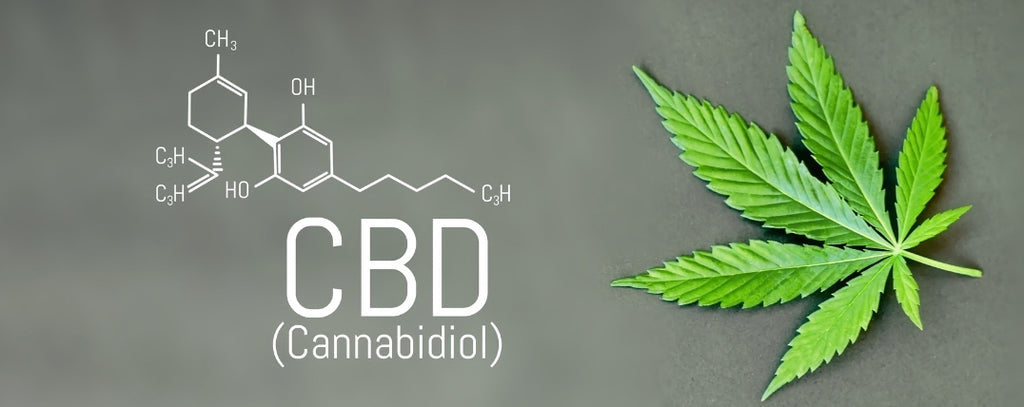
Cannabidiol(CBD - analgesic, antibacterial, lowers blood sugar levels, relieves nausea, anti-inflammatory, is said to inhibit cell growth of tumour cells, antipsychotic, anti-anxiety, antispasmodic, promotes bone growth, immunosuppressive, neuroprotective).
-
Cannabidiolic acid(CBDA - anti-inflammatory, supposed to inhibit cell growth of tumour cells)
-
Cannabinol(CBN - analgesic, sleep-inducing, antispasmodic)
-
Cannabigerol(CBG - antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, is said to inhibit cell growth of tumour cells and promote bone growth)
- Cannabichromene(CBC - analgesic, anti-inflammatory, thought to inhibit cell growth of tumour cells and promote bone growth).
Cannabinoids - especially CBC - are also used in the treatment of stress and anxiety. Cannabinoids can also help regulate blood sugar levels or inhibit the multiplication of bacteria, viruses or fungi. Besides preparations with isolated cannabinoids that contain only one or a few substances, there are also so-called full-spectrum products. These are obtained in a particularly gentle special process and contain a multitude of naturally pure cannabinoids in combination. This is important because it is assumed that the individual substances support each other in their effect and thus have a more intensive effect.
How do cannabinoids work in the human body?
Many cells of the body have so-called cannabinoid receptors. These are docking sites in the outer cell membrane to which cannabinoids can chemically bind. This triggers a reaction in the cell. Cannabinoid receptors are found, for example, on nerve cells, bone and immune cells, but also on cells of the intestine. Wherever cannabinoid receptors are present, cannabinoids can stimulate a cell reaction - for example, that less of a certain enzyme is produced. This makes them potentially important helpers in controlling metabolic processes. The fact that the body reacts to cannabinoids is what led researchers to look for the corresponding receptors in the first place. In the process, they discovered something extremely exciting: the endogenous (body's own) cannabinoid system of humans. Cannabinoid receptors only make sense when the body itself produces a chemically similar substance - and that is exactly what it does! But what does it do with it?
Cannabinoids as messenger substances in the human body
The so-called endocannabinoids are messenger substances that enable communication between cells and thus help to control important body processes. For example, they are involved in pain processing, in the process of falling asleep, in memory processes (also in "unlearning" fear reactions), in the immune system, in bone formation and degradation, in movement control and much more. For example, they can inhibit the growth of tumours or control appetite. And since cannabinoids from hemp look very similar to them chemically, they can also dock onto their receptors to exert similar effects. You see: Cannabinoids are potentially highly helpful substances with a broad spectrum of effects.






